Accounting is a crucial aspect of business operations that is separated into multiple branches, each aimed at different goals. Cost accounting and management accounting are closely related disciplines within the field of accounting, but they have distinct roles and focuses. Management accounting has a far wider application and impact than cost accounting. Thus, by examining every facet of the company both qualitatively and numerically, management accounting may offer an objective view. However, cost accounting only provides a pixel-by-pixel breakdown of the costs associated with each good, service, or procedure. Businesses may maximise their operations, reach strategic objectives, and make well-informed financial decisions by knowing the distinctions between these two. If you are interested in pursuing a CMA course, then this post serves as a quick reference for all students to understand the difference between cost accounting and management accounting.
What is cost accounting?
Cost accounting focuses on the assessment, measurement, accumulation, and presentation of all the costs incurred in providing a particular product or service. Its purpose is to offer specific cost data to management to help in organising, controlling, and decision-making on the costs. It involves tracking costs to different activities in an organisation to assess the efficiency of operation and to identify areas where cost-cutting could be effected together with coming up with the right prices to charge the customers.
Work and responsibility
Cost accounting has a very important function in an organisation, especially in financial matters. Their duties include the following functions, all of which are aimed at monitoring and controlling costs. Here are the primary duties and responsibilities in cost accounting:
1. Cost Recording and Reporting
- Data Collection: Collect information on the material cost, labour cost, and overheads from the concerned departments.
- Record Keeping: An important aspect of cost accounting is the record keeping and documentation of all expenditures linked to the production line and business functioning.
- Cost Reporting: Complete standard cost analysis documents, like cost sheets and production cost reports, so that management can get the best information on cost structures.
2. Cost Analysis and Control
- Cost Analysis: Examine the costs of production processes, define cost influences, and assess the methods of cost distribution.
- Variance Analysis: The second process compares the actual costs of the carried-out activities with standard/budgeted costs and checks out the causes of the possible differences.
- Cost Control: ‘’Promote efficient use of resources to avoid wastage and overspending; costs should not exceed the set budget.’’
3. Budgeting and Forecasting
- Budget Preparation: This includes reporting on the detailed costs and helping in the preparation of budgets.
- Financial Planning: Participate in cost analyses by reviewing and predicting the cost structures of the business in the future.
What is Management accounting?
Management accounting is particularly concerned with the supply of information to higher management to help them make decisions, plan, and control. It comprises the systematic application of tools and methods to measure and interpret organisational financial information to make and support decisions. Also, don’t confuse management accounting with financial accounting, financial accounting provides information to outside users like investors and auditors, while management accounting is mainly for internal users like managers within an organisation to help with their decisions and planning.
Work and Responsibility
The tasks of management accountants, also referred to as managerial accountants, are diverse and revolve around facilitating decision-making by the management departments. Their responsibilities include the following:
1. Strategic Planning
- Long-Term Planning: Support formulation of long-term strategic financial strategies that will correspond to the overall goals of the business.
- Resource Allocation: Offer guidance for the effective management of resources to utilise them in a manner that will allow for the best returns and the achievement of the firm’s overall strategic objectives.
- Competitive Analysis: Explain the positions of buyers and sellers, the competition among businesses and organisations, and other factors to make strategic plans.
2. Financial Analysis and Reporting
- Internal Reporting: Create financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and statements of cash flows for the management.
- Cost Analysis: Cost behaviour analysis, cost structure, cost control, and cost allocation are used to guide how to deal with costs.
- Performance Metrics: Create and track the parameters of the performance of various organisations, goods, and services to assess their efficiency.
3. Decision Support
- Data Analysis: Utilise the financial and operational data to generate information required for strategic and tactical management decisions.
- Business Case Development: Develop conceptual dockets for new projects, investments, or driving initiatives such as cost advantage and disadvantage analysis plus risk evaluation.
- Scenario Planning: Perform the activities associated with using the overall set of tools, including conducting the scenario analysis and the what-if analysis to assess the effect of various business decisions and external conditions.
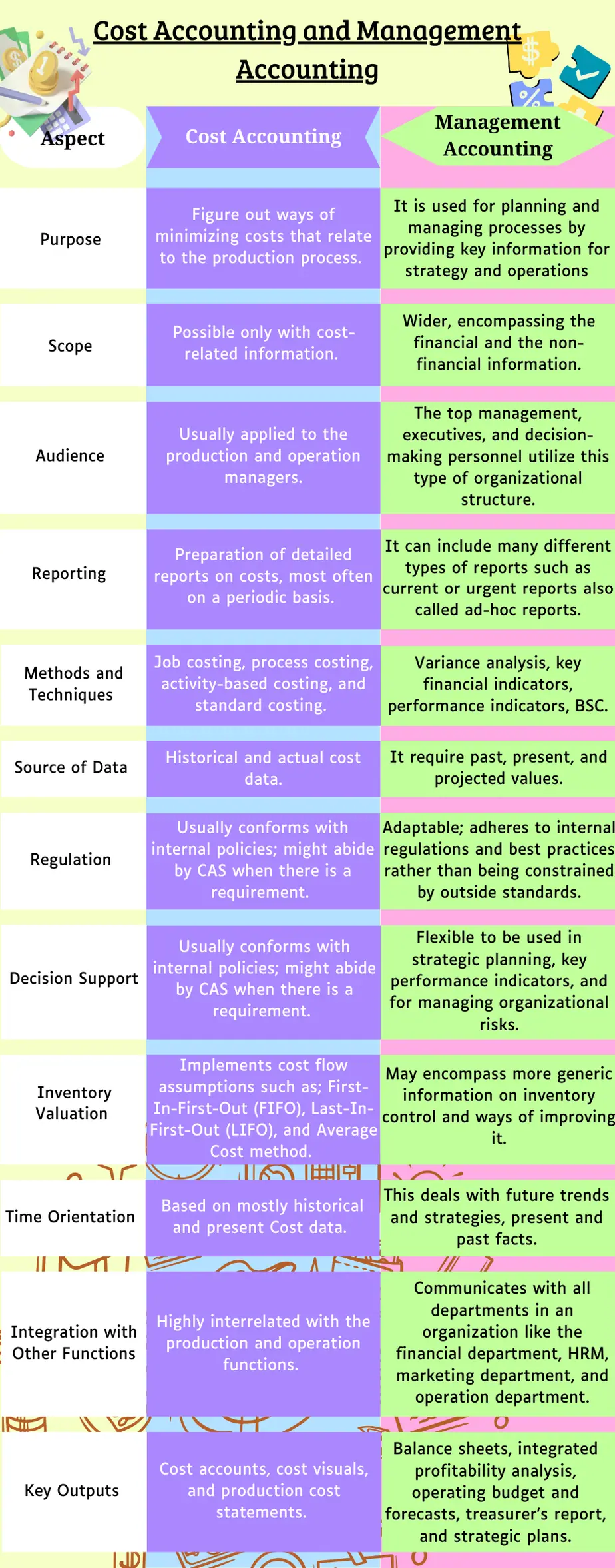
Difference between cost accounting and management accounting
We found a very comprehensive infographic explaining the difference between cost accounting and management accounting.
Conclusion
Accounting includes both cost accounting and management accounting. Students who pursue CMA (cost management accounting) has the capability to work on Cost, financial and management accounting in an organisation. They aid in making sure the company operates smoothly and effectively. The goals of cost accounting are to cut down on additional spending, eliminate unneeded expenses, and manage different costs. However, management accounting focuses on goal-setting, strategy development, policy planning, and other related areas.
If you liked this content we recommend you check our other related articles. For commerce students, these articles will be really helpful.